Ethereum and its Relationship with DVT
Our goal for this page is to equip you with the foundational knowledge needed to actively contribute to the advancement of Obol while also directing you to valuable Ethereum and DVT related resources. Additionally, we will shed light on the intersection of DVT and Ethereum, offering curated articles and blog posts to enhance your understanding.
Understanding Ethereum
To grasp the current landscape of Ethereum's PoS development, we encourage you to delve into the wealth of information available on the Official Ethereum Website. The Ethereum website serves as a hub for all things Ethereum, catering to individuals at various levels of expertise, whether you're just starting your journey or are an Ethereum veteran. Here, you'll find a trove of resources that cater to diverse learning needs and preferences, ensuring that there's something valuable for everyone in the Ethereum community to discover.
DVT & Ethereum
Distributed Validator Technology
"Distributed validator technology (DVT) is an approach to validator security that spreads out key management and signing responsibilities across multiple parties, to reduce single points of failure, and increase validator resiliency.
It does this by splitting the private key used to secure a validator across many computers organized into a "cluster". The benefit of this is that it makes it very difficult for attackers to gain access to the key, because it is not stored in full on any single machine. It also allows for some nodes to go offline, as the necessary signing can be done by a subset of the machines in each cluster. This reduces single points of failure from the network and makes the whole validator set more robust." (ethereum.org, 2023)
Learn More About Distributed Validator technology from The Official Ethereum Website
How Does DVT Improve Staking on Ethereum?
If you haven’t yet heard, Distributed Validator Technology, or DVT, is the next big thing on The Merge section of the Ethereum roadmap. Learn more about this in our blog post: What is DVT and How Does It Improve Staking on Ethereum?
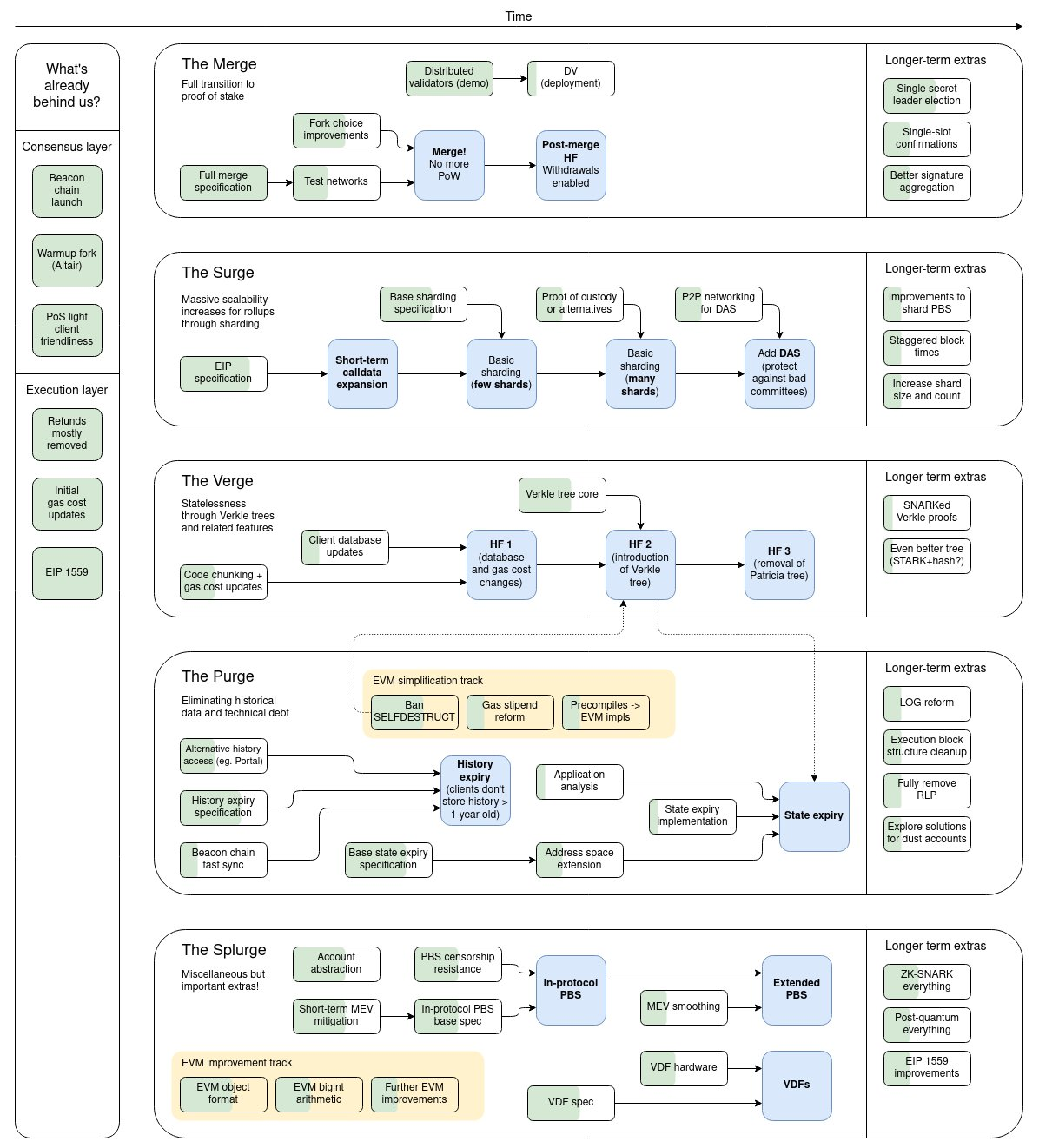
Vitalik's Ethereum Roadmap
Deep Dive Into DVT and Charon’s Architecture
Minimizing correlation is vital when designing DVT as Ethereum Proof of Stake is designed to heavily punish correlated behavior. In designing Obol, we’ve made careful choices to create a trust-minimized and non-correlated architecture.
Read more about Designing Non-Correlation Here
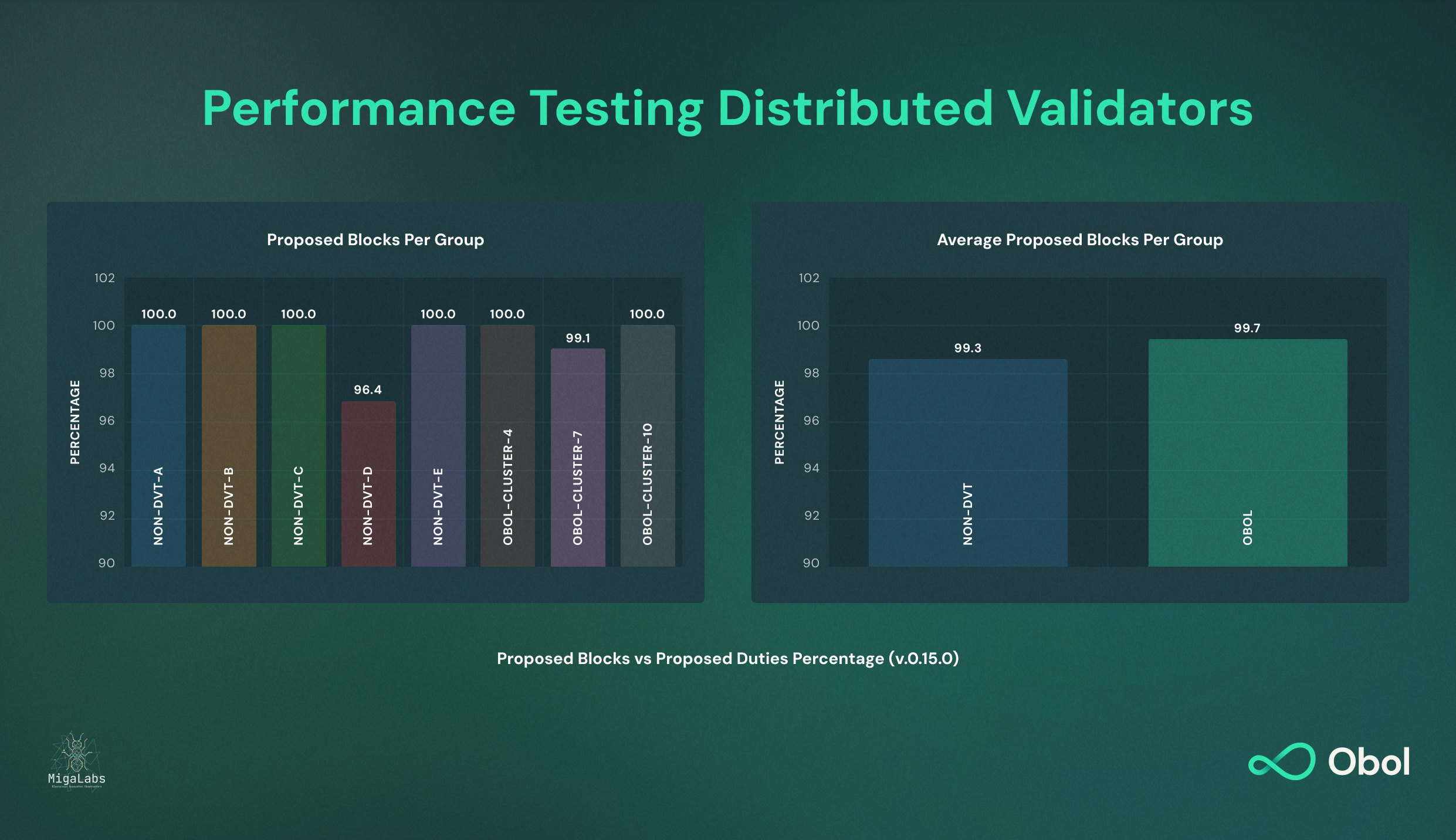
Performance Testing Distributed Validators
In our mission to help make Ethereum consensus more resilient and decentralised with distributed validators (DVs), it’s critical that we do not compromise on the performance and effectiveness of validators. Earlier this year, we worked with MigaLabs, the blockchain ecosystem observatory located in Barcelona, to perform an independent test to validate the performance of Obol DVs under different configurations and conditions. After taking a few weeks to fully analyse the results together with MigaLabs, we’re happy to share the results of these performance tests.
Read More About The Performance Test Results Here
More Resources
- Sorting out Distributed Validator Technology
- A tour of Verifiable Secret Sharing schemes and Distributed Key Generation protocols
- Threshold Signature Schemes
References
- ethereum.org. (2023). Distributed Validator Technology. [online] Available at: https://ethereum.org/en/staking/dvt/ [Accessed 25 Sep. 2023].